Forward Proxy vs Reverse Proxy: The Difference Explained
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on forward proxy and reverse proxy servers. In this article, we will delve into the key differences between these two types of proxy servers and shed light on their significance in network architecture. Whether you’re a network administrator or simply curious about proxy servers, this article will provide valuable insights.
When it comes to securing and optimizing network traffic, understanding the difference between forward proxy and reverse proxy is crucial. Both proxy server types play vital roles in enhancing security measures and improving performance. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of when and how to use each type of proxy server effectively.
In the sections that follow, we will explore the functionality, benefits, and scenarios in which forward proxy and reverse proxy servers are preferred. We will also conduct a comprehensive comparison between the two, addressing factors such as deployment and performance impact on your network. Additionally, we will highlight the specific security considerations associated with each type of proxy server.
Whether you’re a seasoned professional or new to the world of networking, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions when it comes to forward proxy and reverse proxy servers. So, let’s dive in and uncover the differences between these two essential components of network architecture.
Understanding Forward Proxy Servers
In the world of network architecture, proxy servers play a crucial role in enhancing security and optimizing performance. In this section, we will dive deep into the functionality and purpose of forward proxy servers. We will explore when and why they are used, and the valuable contributions they make towards safeguarding network infrastructures.
What is a Forward Proxy Server?
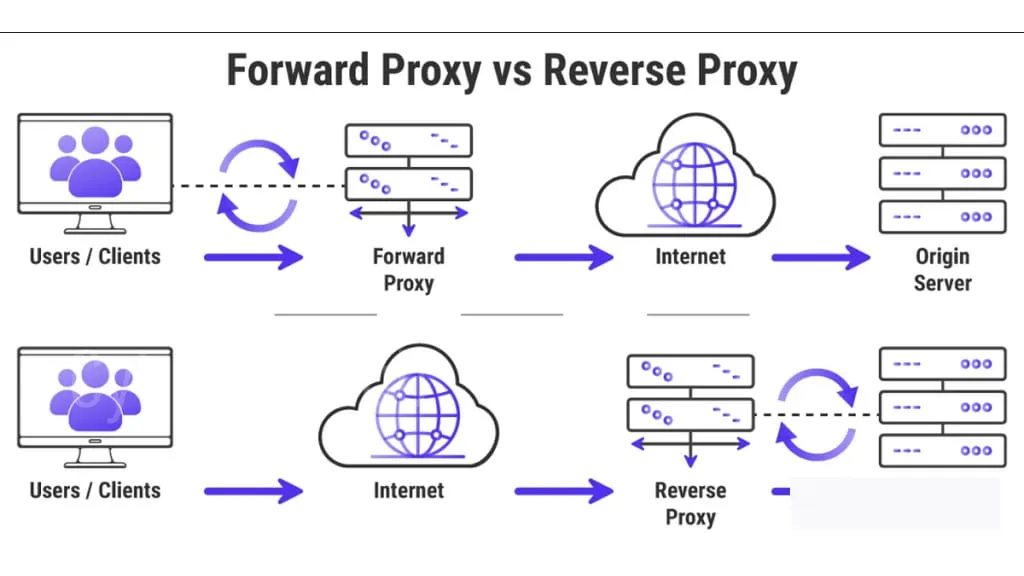
A forward proxy server acts as an intermediary between client devices and the internet. When a user initiates a request to access a website or any online resource, their request is first routed through the forward proxy server. This proxy server then forwards the request on their behalf, keeping the client’s identity hidden from the destination server.
Forward proxy servers are primarily utilized in corporate networks, where they provide a layer of security and control over outbound internet traffic. By acting as a gatekeeper, these proxies enforce access controls, filter content, and monitor user activity. This ensures compliance with company policies and prevents unauthorized access to potentially malicious websites or content.
Benefits of Forward Proxy for Security
Forward proxy servers offer several security benefits:
- Anonymous Browsing: Users’ IP addresses and identities are concealed, making it difficult for websites to track them.
- Content Filtering: Proxy servers can block access to specific websites or types of content, preventing employees from visiting inappropriate or potentially harmful sites.
- Malware Protection: By scanning web traffic, forward proxies can detect and block URLs known to distribute malware, providing an additional layer of defense against cyber threats.
- Privacy: Forward proxies help protect user privacy by encrypting connections, especially when accessing websites over unsecured networks.
When it comes to deciding between a forward proxy and a reverse proxy, the choice depends on the specific use case and network requirements. While forward proxy servers excel at securing outbound traffic, reverse proxies are better suited for safeguarding inbound traffic. In the next section, we will explore the world of reverse proxy servers and uncover their unique advantages.
Reverse Proxy Servers in Focus
In the world of proxy servers, reverse proxies play a crucial role in enhancing network architecture and optimizing performance. While forward proxies are commonly used, there are scenarios where reverse proxies offer distinct advantages over their counterparts.
Key Features of Reverse Proxy Servers
- Acts as an intermediary between client devices and servers by receiving requests on behalf of the server.
- Provides load balancing capabilities by distributing incoming client requests across multiple backend servers.
- Offers caching functionality to improve response times and reduce bandwidth consumption, especially for static content.
- Enhances security by concealing sensitive information about backend servers.
When to Use Reverse Proxy vs Forward Proxy?
Understanding when to use a reverse proxy server versus a forward proxy server is essential for network administrators and IT professionals. Reverse proxies are particularly beneficial in the following cases:
- Load Balancing: Reverse proxies help distribute client requests among multiple servers to ensure optimal performance and prevent overloading of individual servers.
- Web Application Firewall (WAF) Protection: By intercepting and inspecting incoming traffic, reverse proxies can filter out malicious requests and provide an added layer of security for web applications.
- Content Caching: Reverse proxies are capable of caching frequently-accessed static content, reducing the load on backend servers and improving overall response times.
- SSL Termination: Reverse proxies can handle SSL/TLS termination, offloading the decryption process from backend servers and improving their performance.
Benefits of Reverse Proxy over Forward Proxy
When evaluating the benefits of reverse proxy servers in comparison to forward proxies, several advantages emerge:
- Improved performance due to load balancing and caching capabilities.
- Enhanced security through web application firewall protection and SSL termination.
- Reduced strain on backend servers by offloading tasks such as SSL termination and static content delivery.
- Better scalability for handling large volumes of client requests.
With their ability to optimize performance, enhance security, and improve scalability, reverse proxy servers are a valuable tool in modern network architecture.
A Comparison of Proxy Server Types
In today’s digital landscape, businesses often rely on proxy servers to enhance security, optimize network performance, and ensure a seamless browsing experience for their users. Two commonly used types of proxy servers are forward proxy and reverse proxy. While both have their unique advantages, understanding the differences between them is crucial when it comes to selecting the most suitable proxy server for your specific needs.
Functionality
Forward proxy servers act as intermediaries between client devices and the internet. When a user requests a web page or any online content, the forward proxy server forwards the request on behalf of the user, allowing them to access the requested content anonymously. On the other hand, reverse proxy servers sit between client devices and web servers, receiving requests from clients and directing them to the appropriate server in the backend. This indirect connection helps protect the identity and location of the origin server.
Deployment
In terms of deployment, forward proxy servers are typically placed within local networks, allowing multiple users to access the internet via a single IP address. This centralized setup provides enhanced control over user access and content filtering. On the contrary, reverse proxy servers are usually positioned in front of web servers, distributing incoming client requests across multiple servers to optimize load balancing and improve performance.
Impact on Network Performance
When considering network performance, forward proxy servers can enable caching, which stores frequently accessed web content locally. This caching mechanism accelerates subsequent requests for the same content, minimizing the load on the external network. Conversely, reverse proxy servers excel at handling high volumes of incoming client requests by distributing the load across multiple backend servers. This load balancing technique ensures a smoother and more responsive browsing experience for users.
Summary
| Forward Proxy | Reverse Proxy |
|---|---|
| Acts as an intermediary between client devices and internet | Sits between client devices and web servers |
| Deployed within local networks | Positioned in front of web servers |
| Enables caching for faster content retrieval | Optimizes load balancing and improves performance |
By understanding the distinctions between forward proxy and reverse proxy servers, businesses can make informed decisions regarding network architecture. Whether you prioritize enhanced security or improved performance, selecting the appropriate proxy server type is crucial for achieving your desired outcomes.
Security Considerations with Proxies
In today’s digital landscape, ensuring robust security is of paramount importance for businesses and individuals alike. When it comes to proxy servers, security considerations play a crucial role in determining the effectiveness and reliability of the chosen solution. In this section, we will explore the security benefits offered by forward proxies and compare them to reverse proxies, enabling you to make an informed decision based on your specific security requirements.
The Security Benefits of Forward Proxy
Forward proxy servers act as an intermediary between end-users and the internet, intercepting and forwarding requests on their behalf. One of the key security advantages of utilizing forward proxies is the ability to enforce access controls and protect internal networks from external threats.
By routing all internet traffic through a forward proxy server, organizations can implement strict policies and filtering techniques to regulate and monitor user access. This enables network administrators to mitigate potential vulnerabilities and safeguard sensitive data from malicious activities.
Furthermore, forward proxies provide an additional layer of anonymity by masking the originating IP address of clients. This enhanced privacy protection can help prevent unauthorized access and protect user identities in scenarios where anonymity is critical.
Considering Reverse Proxy for Security
While forward proxies excel in certain security aspects, reverse proxies also offer unique benefits that cater to specific security requirements. Reverse proxy servers sit between client devices and backend servers, acting as a gatekeeper and protecting internal resources from direct exposure to the internet.
One of the primary security advantages of reverse proxies is their ability to provide increased resilience against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. By distributing incoming traffic across multiple backend servers, reverse proxies can effectively mitigate the impact of volumetric attacks, ensuring continuous availability and preventing service disruptions.
Reverse proxies also provide advanced load balancing and caching capabilities, optimizing server performance and minimizing the risk of server overloading due to excessive requests. This not only enhances security but also improves user experience by delivering faster responses and reducing latency.
Choosing Forward Proxy for Enhanced Security
While both forward proxies and reverse proxies offer valuable security features, forward proxies often present a more comprehensive solution for organizations with stringent security needs. By implementing access controls, filtering mechanisms, and privacy protection, forward proxies empower businesses to maintain a secure and controlled network environment.
The benefits of forward proxies extend beyond security, as they also contribute to enhanced monitoring and auditing capabilities. By centralizing all internet traffic through the proxy server, organizations can gain better visibility into user activities, detect anomalies, and respond promptly to potential security threats.
In summary, while reverse proxies serve specific security requirements such as load balancing and DDoS protection, forward proxies offer a holistic security solution with strong access controls, privacy protection, and comprehensive monitoring capabilities. By carefully evaluating your security priorities, you can make an informed decision on whether a forward proxy or reverse proxy is the right choice for your organization’s security needs.
Performance Analysis: Forward Proxy vs. Reverse Proxy
When it comes to proxy servers, performance plays a crucial role in determining their effectiveness in supporting network infrastructure. In this section, we will examine the performance implications of utilizing forward proxy and reverse proxy servers. By understanding the impact of these proxy types on network speed, efficiency, and overall user experience, we can make informed decisions about which proxy server best suits our specific needs.
To accurately compare the performance of forward proxy and reverse proxy servers, it is essential to consider several factors:
- Network Latency: Forward proxy servers, while useful for enhancing security, can introduce additional latency due to the additional hop between the client and the requested server. In contrast, reverse proxy servers typically reside closer to the requested server, resulting in lower latency and faster response times.
- Caching Capabilities: Both forward proxy and reverse proxy servers have the ability to cache content, reducing the need to fetch data from the original server repeatedly. However, reverse proxy servers often offer more advanced caching mechanisms, resulting in improved performance by serving cached content directly to clients.
- Load Balancing: Reverse proxy servers are commonly used in load balancing scenarios, distributing incoming requests across multiple backend servers for improved server performance and scalability. Forward proxy servers do not typically incorporate load balancing capabilities, making them less suitable for handling high traffic volumes.
- SSL/TLS Termination: Reverse proxy servers often handle SSL/TLS encryption and decryption on behalf of the backend servers. This offloading process can enhance performance by reducing the computational burden on the backend servers, allowing them to focus on serving content.
It is important to note that the performance of both forward proxy and reverse proxy servers can be influenced by various factors, such as hardware capabilities, network infrastructure, and server configurations. Thus, it is crucial to consider the specific requirements of your network architecture and workload when evaluating performance.
Performance Comparison:
To provide a clearer understanding of the performance differences between forward proxy and reverse proxy servers, let’s examine them in the context of key performance metrics:
| Performance Metric | Forward Proxy | Reverse Proxy |
|---|---|---|
| Network Latency | Higher due to additional hop | Lower due to proximity to backend servers |
| Caching | Basic caching capabilities | Advanced caching mechanisms |
| Load Balancing | Not applicable | Commonly used for load balancing |
| SSL/TLS Termination | Not applicable | Capable of handling SSL/TLS termination |
Based on the performance analysis, it is evident that reverse proxy servers generally offer advantages in terms of network latency, caching capabilities, load balancing, and SSL/TLS termination. However, it is crucial to consider the specific requirements and constraints of your network architecture before deciding whether to implement a forward proxy or a reverse proxy server.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between forward proxy and reverse proxy servers is crucial in optimizing network architecture. By comparing the two types of proxy servers, we have gained valuable insights into their functionality and the benefits they offer.
Forward proxy servers act as intermediaries between clients and servers, enabling secure and anonymous internet browsing. They are commonly used to enhance security measures within a network setup. On the other hand, reverse proxy servers provide load balancing, caching, and improved performance for web applications, making them essential in high-traffic environments.
In selecting the appropriate proxy server type, it is essential to consider specific network requirements. Forward proxy servers are ideal for individual users or smaller networks, offering enhanced security and privacy. In contrast, reverse proxy servers are well-suited for large-scale deployments, optimizing performance and distributing web traffic efficiently.
By weighing the advantages and disadvantages of both forward proxy and reverse proxy servers, organizations can make informed decisions to enhance their network security and overall performance. Whether it is safeguarding user privacy or optimizing web application delivery, understanding the distinctions between these two proxy server types is critical.
FAQ
What is the difference between a forward proxy and a reverse proxy?
A forward proxy acts as an intermediary between clients and the internet. It helps clients access resources on the internet by forwarding their requests and returning the responses. On the other hand, a reverse proxy sits between clients and web servers. It receives client requests and distributes them to multiple servers, allowing for load balancing and enhanced security.
When should I use a forward proxy or a reverse proxy?
You would use a forward proxy when you want to control and monitor outbound traffic from clients in your network. It can be helpful for implementing content filtering, caching, and protecting client anonymity. A reverse proxy is suitable when you want to distribute incoming requests among multiple servers or provide load balancing for improved performance and reliability.
What are the security benefits of using a forward proxy over a reverse proxy?
When using a forward proxy, all client traffic passes through the proxy server, which allows for detailed inspection and filtering. This can help in detecting and blocking malicious content, preventing unauthorized access, and enforcing security policies. In contrast, a reverse proxy primarily offers security benefits through its ability to hide internal server details and provide an additional layer of protection against distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
What are the advantages of using a reverse proxy over a forward proxy?
Reverse proxies offer several advantages, including load balancing, improved scalability, and increased fault tolerance. By distributing requests among multiple servers, a reverse proxy can enhance performance and ensure high availability of web services. It also allows for easy scaling of the server infrastructure without affecting clients.
How do forward proxy and reverse proxy servers differ in terms of performance?
Forward proxies can enhance performance by caching frequently accessed resources, reducing bandwidth usage, and accelerating content delivery to clients. However, they may introduce some latency due to the additional server hops. Reverse proxies, on the other hand, can improve performance through load balancing and providing faster responses by directing requests to the server with the least load. Overall, the impact on performance varies depending on the specific network setup and the optimization measures in place.
