How to Install a VPN on Linux for Online Privacy

Have you ever wondered why your online activities feel less secure on Linux compared to other platforms? While Linux is known for its robust security, protecting your privacy requires extra steps. This is where a VPN becomes essential.
Setting up a VPN on Linux can be tricky. Unlike Windows or macOS, Linux often relies on command-line tools or network settings adjustments. Popular providers like ExpressVPN and NordVPN offer solutions, but the process varies depending on your distribution.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to establish a secure VPN connection. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced user, you’ll find methods tailored to your needs. By the end, you’ll have the tools to mask your location and keep your data safe from prying eyes.
Getting Started with VPN on Linux
Linux users often face unique challenges in maintaining internet security. While the operating system is known for its robustness, privacy concerns persist, especially on public Wi-Fi networks. A VPN can address these issues effectively.

Understanding the Importance of Online Privacy
Public Wi-Fi networks, like those in cafes or airports, are often unencrypted. This makes them vulnerable to hackers. Using a VPN encrypts your connection, ensuring your data remains private. Even in apartment complexes or shared spaces, a VPN can protect your internet activity.
Linux systems rely on command-line tools or network settings adjustments for VPN setup. This can be intimidating for beginners. However, understanding the basics of VPN servers and clients simplifies the process. A VPN server routes your traffic through a secure tunnel, while the client software manages the connection.
Benefits of Using a VPN on Linux
A VPN offers several advantages for Linux users. It bypasses geo-restrictions, allowing access to global content. It also enhances privacy by masking your IP address. Whether you use a dedicated VPN client or native network settings, the benefits are clear.
Choosing the right VPN server and client is crucial. It ensures better performance and ease of use. This article will guide you through practical ways to configure VPN software, whether via GUI or command line.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Bypass Geo-Restrictions | Access content from different regions by connecting to a VPN server in that location. |
| Enhanced Privacy | Encrypts your internet connection, protecting your data from hackers and snoopers. |
| Improved Security | Secures your connection on public Wi-Fi networks, even if they are unencrypted. |
| Flexible Setup | Supports both GUI and command-line tools, catering to different user preferences. |
By understanding these benefits, you’ll be better prepared to set up a VPN on your Linux system. The next sections will provide step-by-step instructions tailored to your needs.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Install a VPN on Linux
Linux offers flexibility, but securing your internet traffic requires the right tools. Whether you’re new to Linux or a seasoned user, setting up a VPN is straightforward with the right steps. Below, we’ll walk you through downloading files, using command line tools, and verifying your connection.
Installing VPN Provider Apps and Downloadable Files
Most VPN providers offer downloadable files for Linux. These files often come in formats like .run, .sh, or .deb. Here’s how to get started:
- Visit your VPN provider’s website and download the appropriate file for your Linux distribution.
- Save the file to a directory where you can easily access it.
- Open your terminal and navigate to the directory containing the file.
Using Command Line Tools and Installer Scripts
Linux users often rely on command line tools for installations. Here’s a simple process:
- Make the file executable using the command:
chmod +x filename. - Run the installer with:
sudo ./filename. - Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the setup.
This method works for most VPN providers, including OpenVPN and others. Ensure your system meets all dependencies for a smooth installation.
Verifying Your VPN Connection
After setup, it’s crucial to verify your connection. Use the terminal command curl ifconfig.me to check your IP address. If it matches the VPN server’s location, your traffic is securely routed.
For troubleshooting, ensure the executable flag is set on files and all dependencies are installed. This ensures a reliable VPN connection on your Linux system.
Configuring VPN with Linux’s Native Network Manager
For Linux users, configuring a VPN doesn’t have to involve complex commands. The native Network Manager provides a graphical interface that simplifies the process. Whether you’re on Ubuntu or another distribution, this tool makes it easy to manage your connections.
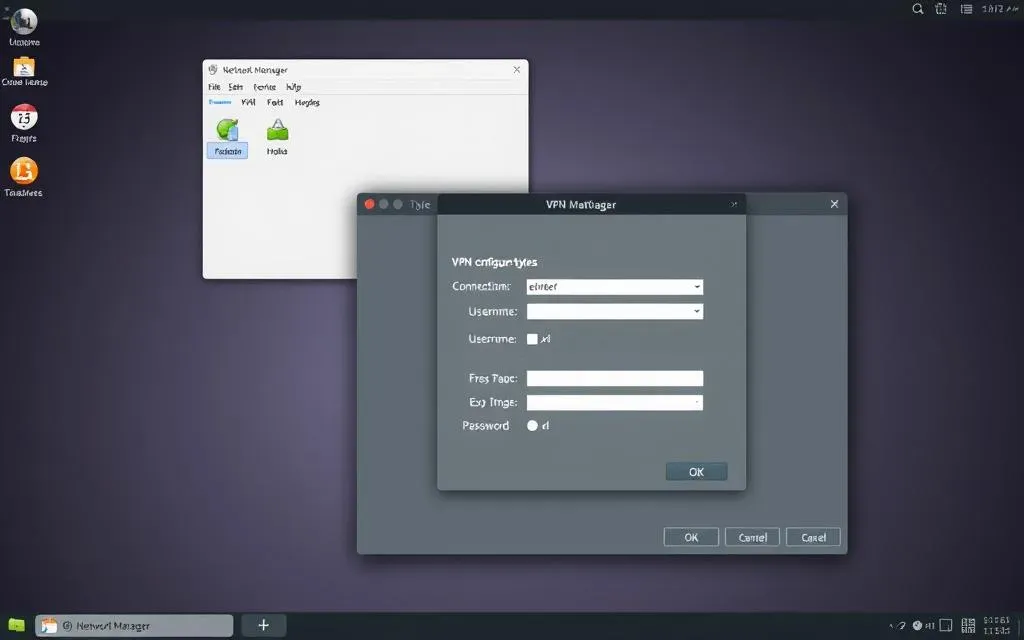
Setting Up a VPN Connection via GUI
To get started, open your network settings from the system menu. Navigate to the VPN section and click “Add.” Here, you’ll select the protocol, such as OpenVPN or WireGuard. Most providers offer detailed instructions for this step.
Next, install any necessary packages. For example, on Ubuntu, you might need the network-manager-openvpn plugin. This ensures compatibility with your chosen protocol. Once installed, you’re ready to configure your connection.
Inputting Accurate VPN Details and Certificates
Accurate details are crucial for a successful connection. Enter the server address, username, and password provided by your VPN provider. If required, upload the certificate file to authenticate your connection.
- Double-check the server location to ensure it matches your desired region.
- Verify the certificate file is correctly uploaded and recognized.
- Save your settings and toggle the connection to activate it.
Using the Network Manager, you can manage multiple VPN profiles on your computer. This is especially useful for users who frequently switch between servers or locations. The GUI also allows you to monitor your connection status and troubleshoot issues visually.
For beginners, this method is a great alternative to command-line tools. It’s intuitive, efficient, and ensures your data remains secure. With the Network Manager, setting up a VPN on Linux becomes a hassle-free experience.
Exploring VPN Protocols and Linux App Options
Choosing the right VPN protocol can significantly impact your online experience. Different protocols offer varying levels of speed, security, and ease of use. For Linux users, understanding these options is key to optimizing your setup.
Comparing OpenVPN, WireGuard, and Other Options
OpenVPN is a popular choice for its strong encryption and compatibility with most systems. However, it can sometimes reduce speed due to its resource-intensive nature. WireGuard, on the other hand, is known for its lightweight design and faster performance, making it ideal for users who prioritize speed.
Other protocols like IKEv2 and L2TP/IPsec also have their strengths. IKEv2 is great for mobile devices, while L2TP/IPsec offers a balance of security and ease of installation. The choice of protocol depends on your specific needs, whether it’s speed, security, or flexibility.
Advantages of Using GUI Versus CLI on Linux
Linux offers both graphical user interface (GUI) and command line interface (CLI) options for managing VPN connections. A GUI-based application, like those provided by NordVPN or ExpressVPN, is user-friendly and ideal for beginners. It simplifies the installation process and allows easy switching between servers.
CLI tools, on the other hand, offer more control and flexibility. They are preferred by advanced users who want to customize their setup. However, they require a steeper learning curve. Both options have their place, and the choice depends on your comfort level and technical expertise.
Regardless of the interface you choose, careful installation and configuration are essential. This ensures maximum privacy and performance. By understanding the strengths of each protocol and interface, you can tailor your VPN setup to suit your needs.
Conclusion
Securing your online presence on Linux doesn’t have to be complicated. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored various methods to set up a VPN, from downloadable provider apps to command-line tools and the native network manager. Each option offers unique benefits, ensuring you can choose the one that best fits your technical comfort level.
We’ve provided practical steps, clear examples, and troubleshooting tips to help you work through the process. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced user, our guide ensures your system remains secure and your data protected. Using a VPN not only enhances privacy but also improves online anonymity over time.
For further support, we recommend checking your VPN provider’s website for updated information. Proper setup is a worthwhile investment in personal security, ready to function in varied computing environments. Follow our guide, and you’ll confidently manage a secure connection on your Linux system.
FAQ
Why should we use a VPN on Linux?
A VPN enhances online privacy by encrypting internet traffic, masking our IP address, and allowing secure access to restricted websites. It’s especially useful for protecting sensitive data on public networks.
Can we install a VPN on Linux without using a GUI?
Yes, we can set up a VPN using command line tools like OpenVPN or WireGuard. These tools provide flexibility and are ideal for server environments or advanced users.
What’s the best VPN protocol for Linux?
OpenVPN and WireGuard are popular choices. OpenVPN is widely supported and secure, while WireGuard offers faster speeds and simpler configuration.
How do we verify if our VPN connection is active?
We can check our IP address using online tools or run commands like `curl ifconfig.me` in the terminal. If the IP matches the VPN server, the connection is active.
Is it possible to configure a VPN using Linux’s Network Manager?
Absolutely. We can set up a VPN connection via the Network Manager GUI by inputting server details, certificates, and authentication credentials.
Are there free VPN options for Linux?
Yes, some providers offer free VPN services, but they often have limitations like slower speeds or data caps. Paid options generally provide better performance and support.
How do we switch between VPN servers on Linux?
We can switch servers by updating the VPN configuration file or using the provider’s app. Some GUI tools also allow easy server switching.
Does using a VPN affect internet speed on Linux?
A VPN may slightly reduce speed due to encryption overhead. However, choosing a high-quality provider and nearby servers minimizes this impact.
Can we use a VPN to bypass geo-restrictions on Linux?
Yes, a VPN allows us to access content restricted by location by routing traffic through servers in different regions.
What’s the difference between GUI and CLI VPN setup on Linux?
GUI tools are user-friendly and ideal for beginners, while CLI offers more control and is preferred for advanced configurations or server setups.
